Fully convolutional networks based models.
Tags:
CV
|
segmentation
Segmentation
Segmentation is a pixel-wise classification task. For example, on the task of cat or dog segmentation, on model output we expects two binary masks with size of source image for each of both classes. Segmentation is of two main types: semantic(e.g. 2 classes: (dog AND cat AND car AND human), background) and semantic(e.g. 5 classes: car, dog, cat, human, bird). Examples of “FCN-like” architectures - Unet, SegNet.
Architecture
The name “Fully convolutional networks” is called so because it fully consists of conv. layers, this model doesn’t use dense layers.
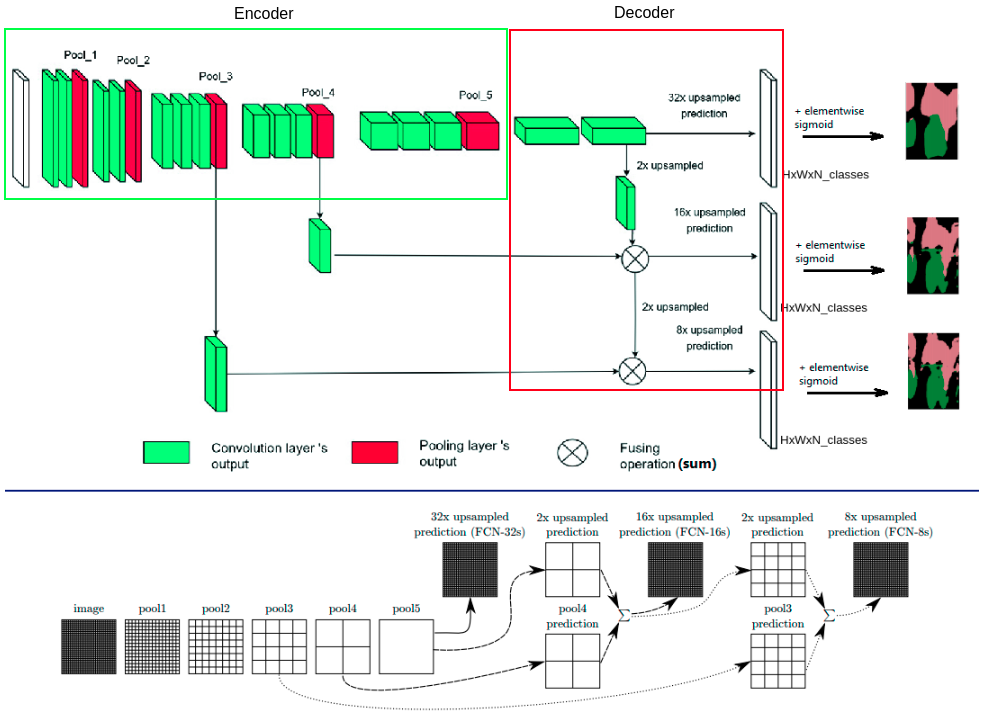
Figure A. Architecture(top), another one visualisation(bottom).
Generally, FCN includes two parts:
- Downsampling(encoder). The first part of the model is encoder or downsampling it using conv/pool layers to get feature maps and it needs to extract different image features[1] from source image, but feature maps received on output of this model part lost positional information about object on image, segmentation based only on the encoder part would be of poor quality, im trying to visualize this on figure A.
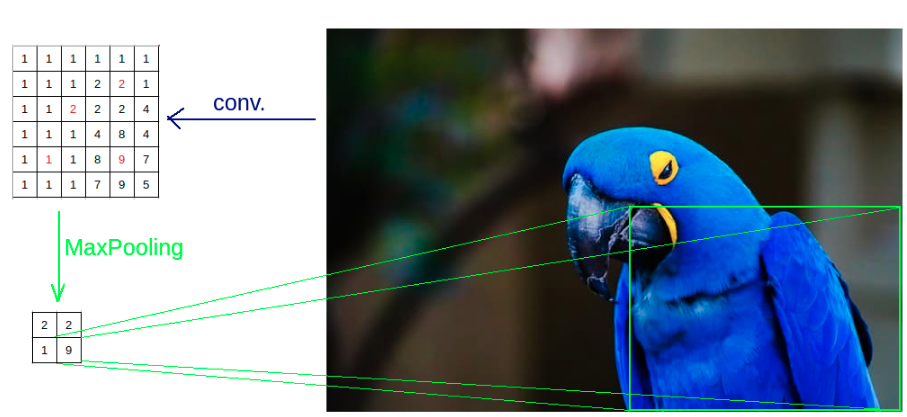
Figure B. Problem of downsample in the context of segmentation task.
- Upsampling or decoder. The second part is decoder its purpose is upsize received feature maps from encoder for recover object positional data. FCN uses deconvolution layers mixed with summation feature maps from early layers for this. Without decoder, feature maps would have low quality(“high pixeled”) segmentation.
Architecture type’s benefits and differences are shown in figure C, FCN-32 using only one 2x deconvolution, FCN-8 - three deconv’s and have better than FCN-32 quality segmentation.
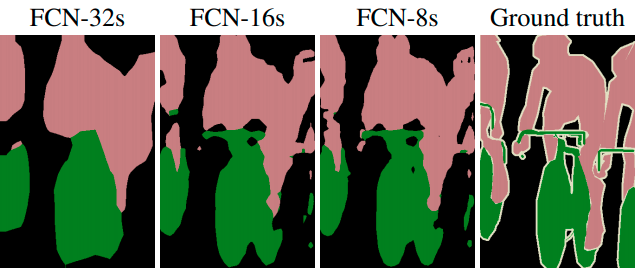
Figure C.
Links